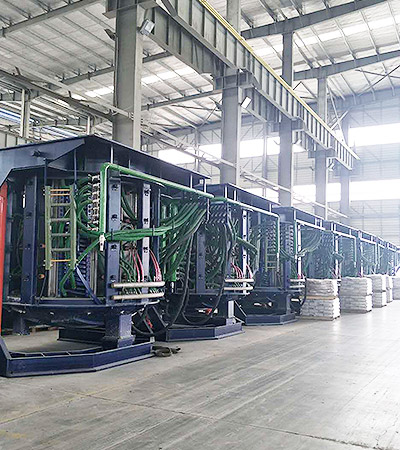
When designing a steel melting furnace, it's important to remember the different factors that influence the process. For example, proper raw material storage is crucial for optimum furnace performance. If scrap is stored on a mud floor, it will quickly become dusty and may cause moisture buildup. Similarly, an inadequately insulated furnace will cause a high power bill and a long cold start cycle.
A high-frequency induction melting furnace should have two separate electrical systems: one for the cooling and tilting systems, and another for the induction coil. The former is fed with a high-voltage electrical line, while the latter is fed with a separate power unit. An induction melting furnace can have operating frequencies ranging from fifty to 10,000 cycles per second. Higher operating frequencies help increase power applied to the furnace while reducing turbulence.
While furnaces can be used to melt different types of materials, metals are the most common. Melted metal is more malleable, making it more easily shaped or reconfigured. This process can improve the quality of the metal product and lower energy costs. Moreover, a furnace can be used to create alloys from scrap, transforming a waste metal into useful products.

Induction melting furnaces are also useful for melting gold, silver, and copper. Depending on the model, they can also be configured to melt steel and other high-temperature alloys. These furnaces have a range of capacities, from four to twelve kilograms of gold to one to five kilograms of steel.
Crucible furnaces are the most basic type of metal furnaces. They use an iron core shaped like a ring and are surrounded by a primary induction coil. The secondary component is made up of loops filled with molten metal. The loops circulate the molten metal, creating a stirring action in the melt.
Electric arc furnaces were developed in the late 1800s. Electric arc furnaces use a high-powered electric current to melt large amounts of steel. Electric arc furnaces are more efficient than other types of furnaces, particularly when it comes to high volume smelting. Many manufacturers of smelting furnaces are now focused on recycling. For example, ZPF produces a high-efficiency aluminum smelting furnace that melts aluminum chips and recycles aluminum ingots.
Another type of steel melting furnace is the channel IF. This type melts all grades of iron, as well as most non-ferrous alloys. It provides high temperature and chemistry control, and is also used for reducing total melting costs. It does not produce any emissions, unlike other types of steelmaking furnaces.
The Bessemer process enables mass production of quality steel. It also allows a higher volume of metal in less time. This is essential for industrial production and the construction of cars, trucks, and other structures.

 English
English España
España EN
EN